
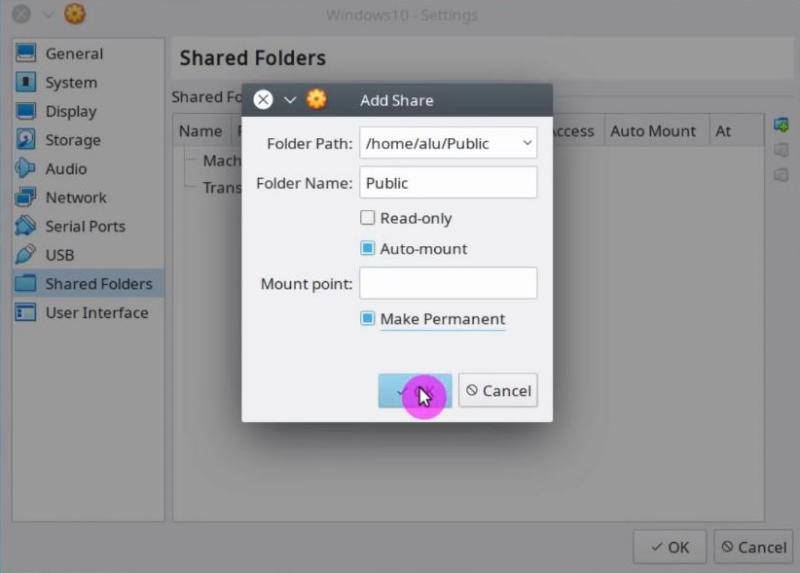
# This boolean parameter controls whether Samba attempts to sync the Unix # running "samba-tool domain provision" to wipe databases and create a # Running as "active directory domain controller" will require first # Most people will want "standalone server" or "member server". # domain controller", "classic backup domain controller", "active # values are "standalone server", "member server", "classic primary Defines in which mode Samba will operate. Panic action = /usr/share/samba/panic-action %d # Do something sensible when Samba crashes: mail the admin a backtrace # Append if you want important messages to be sent to syslog too. # We want Samba to only log to /var/log/samba/log. # Cap the size of the individual log files (in KiB).

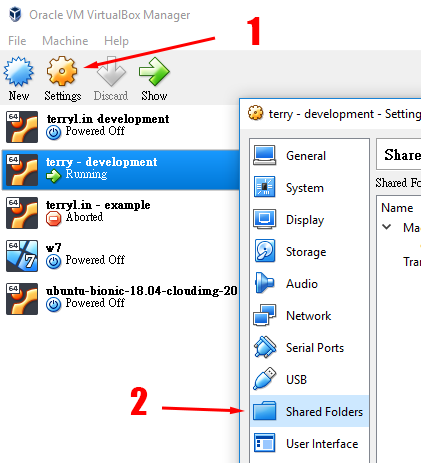
# This tells Samba to use a separate log file for each machine # option cannot handle dynamic or non-broadcast interfaces correctly. # not protected by a firewall or is a firewall itself. # It is recommended that you enable this feature if your Samba machine is # Only bind to the named interfaces and/or networks you must use the # This can be either the interface name or an IP address/netmask # The specific set of interfaces / networks to bind to Server string = %h server (Samba, Ubuntu) # server string is the equivalent of the NT Description field
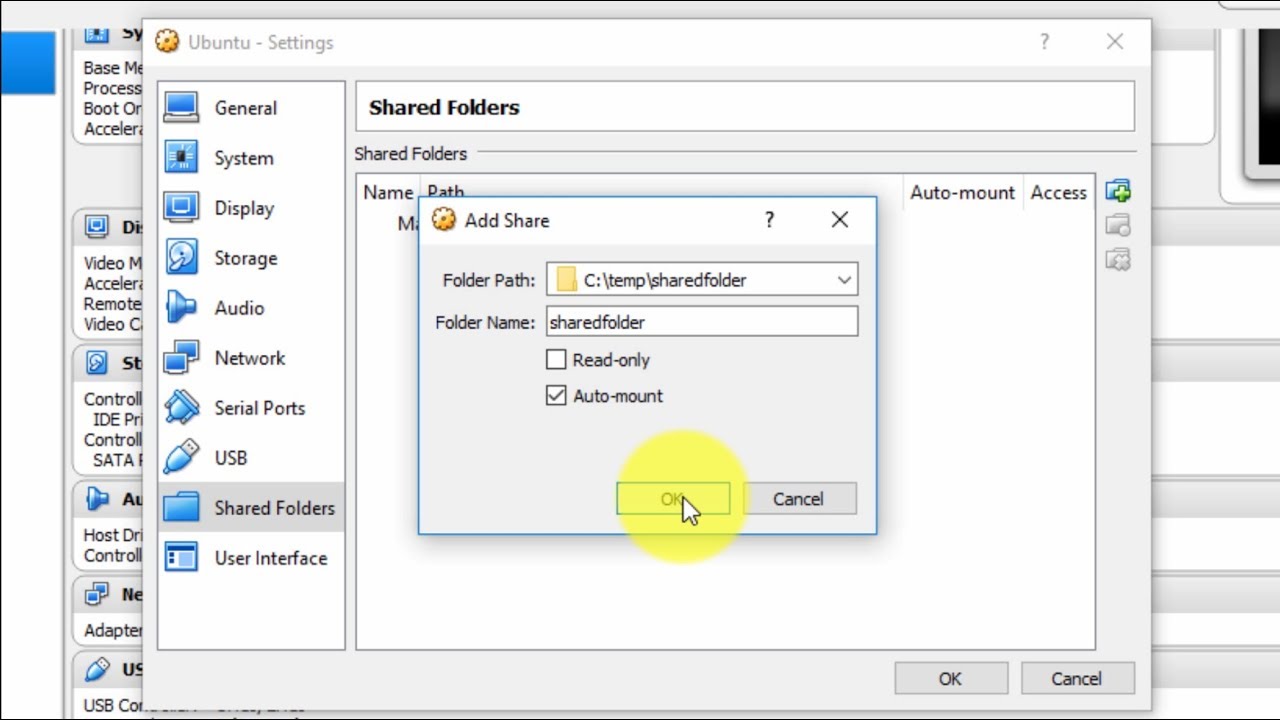
# Change this to the workgroup/NT-domain name your Samba server will part of # "testparm" to check that you have not made any basic syntactic # NOTE: Whenever you modify this file you should run the command # behaviour of Samba but the option is considered important # - When commented with "#", the proposed setting is the default # differs from the default Samba behaviour # - When such options are commented with " ", the proposed setting # Some options that are often worth tuning have been included as Samba has a huge number of configurable options most of which # smb.conf(5) manual page in order to understand the options listed # This is the main Samba configuration file. # Sample configuration file for the Samba suite for Debian GNU/Linux.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
